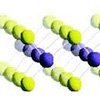
Jan 13, 2025 (Nanowerk News) Combining the best of different crystals to obtain the ultimate material is the motto that drives two-dimensional (2D) materials research. 2D structures are typically built by atomic deposition and weakly bonded to each other by van der Waals interactions. In the last few years, an...
X-ray flashes from a nearby supermassive black hole accelerate mysteriously
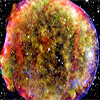
Jan 13, 2025 (Nanowerk News) One supermassive black hole has kept astronomers glued to their scopes for the last several years. First came a surprise disappearance, and now, a precarious spinning act. The black hole in question is 1ES 1927+654, which is about as massive as a million suns and...
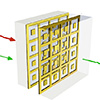
Boosting terahertz signal processing with multilayered graphene designs
Jan 13, 2025 (Nanowerk News) Nonlinear optical processes in the technologically important terahertz (THz) spectral range have gained increasing attention for their potential to revolutionize fields such as wireless communication and signal processing. Among the most extreme phenomena in nonlinear optics is harmonic generation, a process converting optical energy into...
Nanothermometers enable real-time temperature monitoring at molecular scale
Jan 13, 2025 (Nanowerk News) Technological advancements in the simultaneous observation of ultrafine structures and temperature changes in materials are paving the way for the development of advanced materials. This innovation is expected to facilitate the analysis of the correlation between specific structures and the thermodynamic properties of samples. A...
Liquid crystal-powered metasurfaces enable switchable color displays and security features
Jan 13, 2025 (Nanowerk Spotlight) The screens we use every day – from smartphones to televisions – work by either filtering white light or creating their own illumination. These approaches have served well but face inherent limitations in displaying rich, vivid colors while keeping power consumption low. Nature offers an...
New study unveils breakthrough in understanding cosmic particle accelerators
Jan 13, 2025 (Nanowerk News) Scientists have come a step closer to understanding how collisionless shock waves – found throughout the universe – are able to accelerate particles to extreme speeds. These shock waves are one of nature's most powerful particle accelerators and have long intrigued scientists for the role...